توضیحات
تحقیق شبکه های حسگر بی سیم زیر آب
شبکه های سنسور زیر آب UWSN[1]در سال های اخیر توجه محققان را به خود واداشته است. این شبکه ها به دلیل کاربرد بسیاری که در حوزه های مختلف دارند دارای اهمیت بسیاری هستند. این شبکه ها برای کشف ناشناخته ها در اعماق زمین و کاربردهای زمین شناسی و نظامی و ….. به کار میروند.
پروتکل های مختلف مسیریابی برای بهبود تحویل بسته با حداقل انرژی و هزینه های تاخیر در UWSN ها پیشنهاد شده اند، که در آن پروتکل های مسیریابی حریص به دلیل سادگی استفاده در بین روش های دیگر دارای اهمیت بیشتری هستند. مسیریابی حریم خصوصی جغرافیایی (همچنین مبتنی بر موقعیت یا مبتنی بر موقعیت مکانی) یک اصل مسیریابی است که براساس اطلاعات موقعیت جغرافیایی برای فرستادن بسته های داده اقدام میکند.
از دیدگاه پروتکل های مسیریابی در شبکه های سنسور زیر آب (UWSNs)، وجود ارتباط از دست رفته، جایی که بسته را نمی توان با استفاده از حالت حریصانه ارسال کرد، شاید مسئله چالش برانگیز باشد.
در سمینار پیش رو ضمن معرفی شبکه های سنسور زیر آب و معرفی مناطق خالی، انواع پروتکل های مسیریابی در این حالت را معرفی و بررسی خواهیم کرد.
…
فهرست مطالب تحقیق شبکه های حسگر بی سیم زیر آب
- 1-1-مقدمه: 9
- 1-2-بیان مسئله: 9
- 1-3-ساختار سمینار: 9
- 2-1-مقدمه: 12
- 2-2-اجزا شبکه حسگر زیر آب: 12
- 2-3-معماری داخلی گره ها: 13
- 2-4-انواع شبکه حسگر زیر آب: 13
- 2-5-چالش های شبکه حسگر بیسیم زیر آب: 15
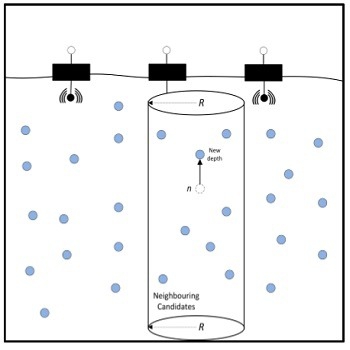
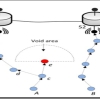
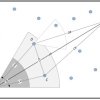
- 2-6-نواحی حفره ای یا خالی در شبکه: 16
- 3-1-مقدمه: 19
- 3-2-انواع مناطق خالی: 19
- 3-3-روش های نادیده گرفتن نودهای دور از دسترس: 20
- 3-3-1-پروتکل VBF: 20
- 3-3-2-پروتکل HH-VBF: 21
- 3-3-3-پروتکل RHHVBF: 22
- 3-3-4-پروتکل RDBF: 23
- 3-3-5-پروتکل ارتباطی DBR: 24
- 3-4-روش های مدیریت نودهای دور از دسترس: 25
- 3-5-تقسیم بندی تکنیک های مدیریت نواحی خالی: 29
- 3-6-تقسیم بندی تکنیک های مدیریت مناطق دور از دسترس: 32
- 3-6-1-پروتکل VBVA: 33
- 3-6-2-پروتکل AHH-VBF: 34
- 3-6-3-پروتکل DFR: 34
- 3-6-4-پروتکل FBR: 35
- 3-6-5-پروتکل RMTG: 36
- 3-6-6-پروتکل MOBICAST: 37
- 3-6-7-پروتکل LLSR: 39
- 3-6-8-پروتکل OVAR و IVAR: 39
- 3-6-9-پروتکل DCR: 40
- 3-6-10-پروتکل GR+DTC: 41
- 3-6-11-پروتکل HYDROCAST: 42
- 3-6-12-الگوریتم VAPR: 42
- 3-6-13-پروتکل WDFAD-DBR: 43
- 3-7-مقایسه پروتکل ها: 43
- 4-1-مقدمه: 47
- 4-2-روش پیشنهادی: 47
- 4-3-پارامترهای ارزیابی: 49
- 4-4-نتیجه گیری: 49
منابع تحقیق شبکه های حسگر بی سیم زیر آب
[1] M. Ayaz, A. Abdullah, I. Faye, and Y. Batira, “An efficient dynamic addressing based routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks,” Comput. Commun., vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 475–486, 2012.
[2] N. Goyal, M. Dave, and A. K. Verma, “Fuzzy based clustering and aggregation technique for Under Water Wireless Sensor Networks,” in Electronics and Communication Systems (ICECS), 2014 International Conference on, 2014, pp. 1–5.
[3] T. Ali, L. T. Jung, and I. Faye, “End-to-End Delay and Energy Efficient Routing Protocol for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks,” Wirel. Pers. Commun., vol. 79, no. 1, pp. 339–361, 2014.
[4] T. Liaqat, N. Javaid, S. M. Ali, M. Imran, and M. Alnuem, “DepthBased Energy-Balanced Hybrid Routing Protocol for Underwater WSNs,” 2015 Int. Conf. Intell. Netw. Collab. Syst., pp. 262–267, 2015.
[5] O. Gaddour, A. Koubâa, N. Baccour, and M. Abid, “OF-FL: QoSaware fuzzy logic objective function for the RPL routing protocol,” in Modeling and Optimization in Mobile, Ad Hoc, and Wireless Networks (WiOpt), 2014 12th International Symposium on, 2014, pp. 365–372.
[6] N. Singh and L. Shrivastava, “Impact of Antenna model with the variation of speed for Reactive and Hybrid routing protocols in Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks,” 2015.
[7] M. C. Domingo, “A distributed energy-aware routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks,” Wireless Personal Communications,vol.57,no.4,pp.607–627,2011
[8] S. Mitra and A. Roy, “Communication void free routing protocol in wireless sensor network,” Wireless Personal Communications, vol. 82, no. 4, pp. 2567–2581, 2015.
[9] S. Basagni, C. Petrioli, R. Petroccia, and D. Spaccini, “Carp: a channelaware routing protocol for underwater acoustic wireless networks,” Ad Hoc Networks, vol. 34, pp. 92–104, 2015.
[10] Heidemann, J., Stojanovic, M. and Zorzi, M. (2012) Underwater Sensor Networks: Applications, Advances, and Challenges. Royal Society, 370, 158-175
[11] G. Han, J. Jiang, N. Bao, L. Wan, and M. Guizani, “Routing protocols for underwater wireless sensor networks,” IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 53, no. 11, pp. 72–78, 2015.
[12] I. Stojmenovic, “Position-based routing in ad hoc networks,” IEEE communications magazine, vol. 40, no. 7, pp. 128–134, 2002.
[13] X. Fan and F. Du, “An efficient bypassing void routing algorithm for wireless sensor network,” Journal of Sensors, vol. 2015, Article ID 686809, 9 pages, 2015. doi:10.1155/2015/686809.
[14] P. Xie, J.-H. Cui, and L. Lao, “VBF: vector-based forwarding protocol for underwater sensor networks,” in Networking 2006. Networking technologies, services, and protocols; performance of computer and communication networks; mobile and wireless communications systems, Springer, 2006, pp. 1216–1221
[15] Chen Wang1,2,Gang Zhang1,2,Yang Shao1,Lei Zhang1,” IMPROVEMENT RESEARCH OF UNDERWATER SENSOR NETWORK ROUTING PROTOCOL HHVBF”, Journal of Sensors, vol. 2015, 15632, 9 pages, 2015.
[16] ZonglinLi,NianminYao,andQinGao,” Relative Distance Based Forwarding Protocol for Underwater Wireless Networks”,Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks Volume 2014, Article ID 173089, 11 pages.
[17] Hai Yan, Zhijie Jerry Shi, and Jun-Hong Cui,” DBR: Depth-Based Routing for Underwater Sensor Network”, Distributed Sensor Networks Volume16 –PP 8, 2014
[18] Seyed Mohammad Ghoreyshi, Alireza Shahrabi, and Tuleen Boutaleb,” Void-Handling Techniques for Routing Protocols in Underwater Sensor Networks: Survey and Challenge”, 1553-877X (c) 2016 IEEE.
[19] X. Wu, G. Chen, and J. Chen, “Energy-efficient and topology-aware routing for underwater sensor networks,” in Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN), Zurich, Switzerland, pp. 1–6, IEEE, 2010.
[20] J. Jiang, G. Han, H. Guo, L. Shu, and J. J. Rodrigues, “Geographic multipath routing based on geospatial division in duty-cycled underwater wireless sensor networks,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 59, pp. 4–13, 2016
[21] Peng Xie, Zhong Zhou, Zheng Peng, Jun-Hong Cui and Zhijie Shi,” Void Avoidance in Mobile Underwater Sensor Networks”, In IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, volume 12, Oct. 2015.
[22] H. Yu, N. Yao, and J. Liu, “An adaptive routing protocol in underwater sparse acoustic sensor networks,” Ad Hoc Networks, vol. 34, pp. 121– 143, 2015.
[23] Dongseung Shin1, Daeyoup Hwang2 and Dongkyun Kim3,” DFR: an efficient directional flooding-based routing protocol in underwater sensor network”, WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND MOBILE COMPUTING Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2012; 12:1517–1527.
[24] J. M. Jornet, M. Stojanovic, and M. Zorzi, “Focused beam routing protocol for underwater acoustic networks,” in Proceedings of the third ACM international workshop on Underwater Networks, San Francisco, California, USA, pp. 75–82, ACM, 2008.
[25] S. K. Dhurandher, M. S. Obaidat, and M. Gupta, “A novel geocast technique with hole detection in underwater sensor networks,” in ACS International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Hammamet, Tunisia, pp. 1–8, IEEE, 2010.
[26] Y.-S. Chen and Y.-W. Lin, “Mobicast routing protocol for underwater sensor networks,” IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 737–749, 2013.
[27] M. Barbeau, S. Blouin, G. Cervera, J. Garcia-Alfaro, and E. Kranakis, “Location-free link state routing for underwater acoustic sensor networks,” in 28th Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Halifax, Canada, pp. 1544–1549, IEEE, 2015
[28] S. M. Ghoreyshi, A. Shahrabi, and T. Boutaleb, “A novel cooperative opportunistic routing scheme for underwater sensor networks,” Sensors, vol. 16, no. 3, p. 297, 2016.
[29] R. W. Coutinho, L. F. Vieira, A. Loureiro, et al., “Dcr: Depth-controlled routing protocol for underwater sensor networks,” in IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications, Split, Croatia, pp. 453–458, IEEE, 2013
[30] R. W. Coutinho, A. Boukerche, L. F. Vieira, and A. A. Loureiro, “A novel void node recovery paradigm for long-term underwater sensor networks,” Ad Hoc Networks, vol. 34, pp. 144–156, 2015.
[31] U. Lee, P. Wang, Y. Noh, F. Vieira, M. Gerla, and J.-H. Cui, “Pressure routing for underwater sensor networks,” in 29th conference on Information communications (INFOCOM), San Diego, California, USA, pp. 1676–1684, 2010
[32] Y. Noh, U. Lee, P. Wang, B. S. C. Choi, and M. Gerla, “Vapr: void-aware pressure routing for underwater sensor networks,” IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 895–908, 2013.
[33] H. Yu, N. Yao, T. Wang, G. Li, Z. Gao, and G. Tan, “Wdfad-dbr: Weighting depth and forwarding area division dbr routing protocol for uasns,” Ad Hoc Networks, vol. 37, pp. 256–282, 2016
توجه:
تحقیق شبکه های حسگر بی سیم زیر آب شامل یک فایل ورد 60 صفحه ای می باشد.
لینک دانلود فایل بلافاصله پس از خرید بصورت اتوماتیک برای شما ایمیل می گردد.
به منظور سفارش تحقیق مرتبط با رشته تخصصی خود بر روی کلید زیر کلیک نمایید.
سفارش تحقیق










نقد و بررسیها
هنوز بررسیای ثبت نشده است.